Table of Content
Single Sign-On (SSO) is a technology that allows users to authenticate themselves once and gain access to multiple applications and systems without having to re-enter their credentials. This technology has become increasingly popular as organizations seek to streamline their authentication processes and improve user experience. SSO can be implemented in various ways, including tokens, cookies, and federation protocols.
One of the primary benefits of SSO is that it reduces the number of passwords that users need to remember and manage. This can help to improve security, as users are less likely to use weak or easily guessable passwords. SSO can also reduce the burden on IT departments, as they no longer have to manage multiple sets of user credentials. Additionally, SSO can improve user experience by allowing users to seamlessly move between different applications and systems without having to log in repeatedly.
Overall, SSO is a powerful technology that can help organizations improve security, streamline authentication processes, and enhance user experience. As such, it is becoming increasingly popular in a wide range of industries and applications.
Understanding SSO
Concept of Single Sign-On
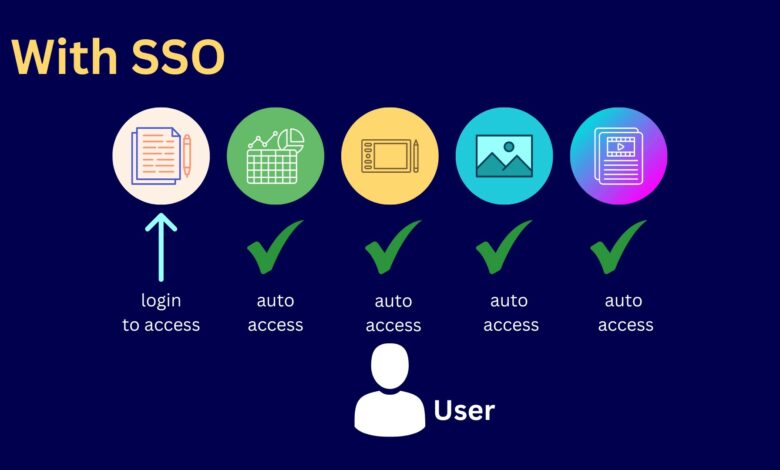
Single Sign-On (SSO) is a user authentication process that allows a user to access multiple applications or systems with a single set of login credentials. This means that a user only needs to enter their login information once, and they are automatically authenticated for all the applications or systems that are part of the SSO network.
SSO works by creating a trust relationship between the identity provider (IDP) and the service provider (SP). When a user logs in to the IDP, the IDP sends the user’s authentication information to the SP, which then grants access to the user without requiring them to enter their login credentials again.
Benefits of SSO
Single Sign-On provides several benefits for both users and organizations. For users, SSO eliminates the need to remember multiple login credentials, making it easier and more convenient to access different applications and systems. For organizations, SSO improves security by reducing the risk of password reuse and simplifying the management of user accounts.
Single Sign-On also helps organizations streamline their user management processes, reducing the time and resources required to manage user accounts across multiple systems. Additionally, SSO can improve productivity by reducing the time it takes for users to access the applications and systems they need to perform their job functions.
Common SSO Protocols
Several Single Sign-On protocols are commonly used in the industry, including SAML, OAuth, OpenID Connect, and Kerberos. SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) is a widely adopted protocol for SSO, which is used to exchange authentication and authorization data between the IDP and SP. OAuth and OpenID Connect are newer protocols that are designed for web-based applications and mobile devices, and they provide more flexibility and security than SAML. Kerberos is an authentication protocol mainly used in enterprise environments to provide Single Sign-On for Windows-based systems.
Overall, it is a powerful tool that can help organizations improve security, streamline user management processes, and enhance productivity. By understanding the concept of Single Sign-On and the benefits it provides, organizations can make informed decisions about whether to implement Single Sign-On in their environment and which Single Sign-On protocol to use.
Implementing Single Sign-On
Single Sign-On is a technique that allows users to access multiple applications with a single set of credentials. This section will discuss the implementation of SSO in an organization.
Single Sign-On Integration Strategies
Several strategies are available for integrating Single Sign-On into an organization’s infrastructure. One approach is to use a cloud-based identity provider such as Okta, OneLogin, or Azure Active Directory. These providers offer pre-built connectors to popular applications such as Salesforce, Box, and Slack, making it easy to set up SSO for these applications. Another approach is to use an on-premise identity provider such as Microsoft Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) or PingFederate. These solutions require more configuration but offer greater control over the SSO process.
Security Considerations
Implementing Single Sign-On requires careful consideration of security risks. Organizations must ensure that the identity provider is secure and that user credentials are protected. It is recommended to use multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security. Additionally, organizations should ensure that their applications support SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) or another secure protocol for exchanging authentication and authorization data.
User Experience and SSO
Single Sign-On can improve the user experience by reducing the number of login prompts and making it easier to access applications. However, organizations need to ensure that the SSO process is seamless and transparent to the user. Organizations should consider customizing the login page to match their branding and provide clear instructions for accessing applications. Additionally, organizations should provide a fallback mechanism in case the Single Sign-On process fails.
In conclusion, implementing Single Sign-On can improve security and user experience in an organization. By choosing the right integration strategy, considering security risks, and focusing on user experience, organizations can successfully implement SSO and reap its benefits.